Ramayana
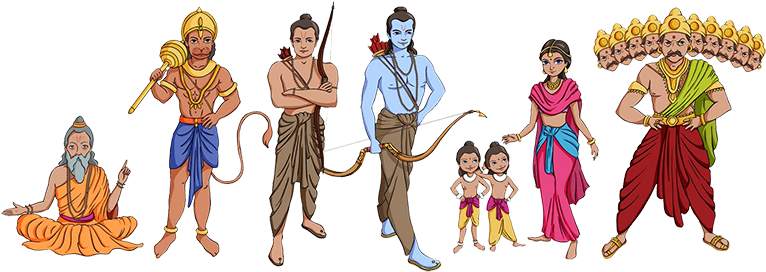
The Eternal Journey of Virtue, Devotion, and Triumph
Introduction:
Ramayana, one of the most revered and widely read epics in the world, is an extraordinary tale of adventure, love, and righteousness. Composed by the sage Valmiki, this ancient Indian epic unfolds the life of Prince Rama, his virtuous wife Sita, and their loyal allies in the face of daunting challenges. The Ramayana serves as a beacon of moral and ethical values, offering profound insights into human nature, the power of devotion, and the triumph of good over evil. In this article, we will embark on an exploration of the key themes, characters, and teachings of the Ramayana, understanding its enduring significance in shaping cultural, social, and spiritual landscapes.
The Setting and Plot:
Set in the ancient kingdom of Ayodhya, the Ramayana revolves around the life of Prince Rama, the seventh avatar of Lord Vishnu, and his divine consort, Sita. The epic begins with the grand preparations for Rama’s coronation as the heir to the throne. However, due to a series of political intrigues, Rama is exiled to the forest for fourteen years, accompanied by his devoted wife Sita and loyal brother Lakshmana.
During their exile, Rama, Sita, and Lakshmana encounter various sages, mythical creatures, and adversaries. The most formidable of these is the demon king Ravana, who abducts Sita and takes her to his island kingdom, Lanka. The epic reaches its climax with Rama’s gathering of an army of monkeys, led by the mighty Hanuman, to rescue Sita from Ravana’s clutches. The ensuing battle between Rama’s forces and Ravana’s demonic army culminates in a cataclysmic confrontation, resulting in Rama’s victory and the triumphant return to Ayodhya.
Key Characters:
The Ramayana introduces a rich cast of characters, each with their unique qualities and roles in the epic’s narrative. Here are some of the central figures:
Rama
The epitome of virtue, Rama is depicted as the perfect son, husband, and king. His unwavering adherence to dharma (righteousness) and his embodiment of ideal qualities make him the central hero of the epic.
Sita
Sita personifies grace, purity, and devotion. As Rama’s wife, she remains steadfast in her love and loyalty, even in the face of adversity. Her abduction by Ravana sets in motion the epic’s central conflict.
Lakshmana
Rama’s loyal brother and companion, Lakshmana embodies selfless service and unwavering devotion. He accompanies Rama during his exile and plays a pivotal role in the rescue of Sita.
Hanuman
The mighty monkey god, Hanuman, is known for his boundless devotion and unwavering loyalty to Rama. His role as the messenger between Rama and Sita and his pivotal contributions during the war make him a beloved character.
Ravana
The powerful demon king and antagonist, Ravana, represents arrogance, lust, and greed. His desire for Sita and his eventual downfall at the hands of Rama serve as cautionary tales of the consequences of hubris.
Themes and Teachings:
The Ramayana teaches us that not only is it possible, but it is also necessary to ensure victory over evil forces. Lord Ram is the epitome of kindness, compassion, and love. His wisdom and patience made it possible for him to follow his inner good without worrying about the loss of luxuries and kingship.
Dharma and Virtue
The Ramayana places a strong emphasis on upholding dharma and virtuous conduct. The epic highlights the importance of fulfilling one’s duties and the challenges faced when navigating moral dilemmas.
Devotion and Surrender
The power of unwavering devotion and surrender to a higher power is a recurring theme in the Ramayana. Characters like Hanuman and Sita exemplify the strength and transformative nature of surrendering to divine will.
Good versus Evil
The epic vividly portrays the eternal battle between good and evil, underscoring the triumph of righteousness over wickedness. Rama’s victory over Ravana symbolizes the ultimate victory of light over darkness.
Loyalty and Brotherhood
The Ramayana celebrates the values of loyalty, brotherhood, and the unwavering support of allies. The bond between Rama, Lakshmana, and Hanuman exemplifies the strength of these relationships.
Sita’s Purity and Women’s Empowerment
Sita’s purity, loyalty, and resilience are held in high regard in the Ramayana. The epic presents a complex exploration of gender dynamics and challenges societal norms surrounding women’s roles and empowerment.
Relevance in the Modern World:
The Ramayana continues to hold immense relevance in the modern world, transcending time and cultural boundaries. Its teachings on righteousness, devotion, and moral conduct serve as guiding principles for individuals seeking to lead virtuous lives. The epic’s portrayal of the eternal battle between good and evil resonates with people navigating the complexities of a morally ambiguous world.
The Ramayana also offers valuable insights into relationships, emphasizing the significance of loyalty, devotion, and mutual support. Its exploration of women’s empowerment and the complex dynamics of gender roles sparks reflection and encourages a deeper understanding of societal norms.
Furthermore, the Ramayana serves as a source of spiritual inspiration, inviting individuals to cultivate devotion, surrender, and selfless service. The epic’s enduring popularity, retellings, and adaptations across various art forms bear testament to its timeless appeal.
Conclusion:
The Ramayana stands as an immortal epic that continues to captivate hearts and minds across generations. Its timeless teachings on dharma, devotion, and the triumph of good over evil offer invaluable insights into the complexities of human nature and the pursuit of righteousness. The epic’s beloved characters and their journeys serve as moral compasses, guiding individuals on the path of virtue and self-realization.
Through its powerful narrative, the Ramayana instills a sense of hope, reminding readers of the indomitable strength of love, faith, and righteousness. It remains a cherished treasure trove of wisdom, cultural heritage, and spiritual guidance, inspiring countless individuals to embody the virtues and values exemplified by Rama, Sita, and the other iconic characters.
Editor – Kaalchakra Team
[ Note – Before Concluding anything as a Finale, Please Go through Original Scriptures of Vaidik Literature Written in Sanskrit and Also with Meaning of That time of Language. Because English is a Limited language to Explaining the Deeper Knowledge of Vaidik Kaal. ]
|| Reference & Reading ||
Shrimad Valmiki Ramayana – Hindi Translation – by Geeta Press – Read Here | Download
Shri Ramcharitmanas – Hindi & Sanskrit – by Goswami Tulsidas – Tulsi Granthavali – Khanda 01 | Khanda 02
Ramcharitmanas (Easy Translation in Hindi) – by Geeta Press – Read Here / Download
Srimad Valmiki Ramayana Of Maharshi Valmiki ( Sachitra, Hindi Translation) – Khanda 01 | Khanda 02
Shri Ramcharitra Manas – by Tulsidas Goswami – Translation by Shri Hanuman Prasad Poddar – Full Book
Ramayana Of Tulsi Das – English Version – by F. S. Growse – Read Here | Other Version
Ramcharitmanas – Hindi Translation by Sitaram Mishra – Written by Tulsi Das – Volume 01 | Volume 02
Ramayana Of Valmiki – With Tilaka Commentary ( Sanskrit) Edited By Vasudeva Laxmana Shastri Pansikar, 1983, Delhi Indological Book House, Delhi – Volume 01 | Volume 02
Srimad Valmiki Ramayana ( With Sanskrit Text And English Trans.) ( Balakanda, Ayodhya Kanda, Aranya Kanda And Kishkinda Kanda) Part 1 Gita Press, Gorakhpur – Volume 01 | Volume 02 | Other Version
The Ramayana of Valmiki, translated by Hari Prasad Shastri – 3 Volumes Combined – 1709 Pages, with complete Outline – Read Here
The Ramayana – English Version – by Manmatha Nath Dutt – Bala Kanda | Ayodhya Kanda | Aranya Kanda | Kishkindha Kanda | Sundara Kanda | Yuddha Kanda | Uttara Kanda | All 7 Kand Collection
The Ramayana – English Modernised Version – by Makhan Lal Sen – Volume 01 | Volume 02 | Volume 03
|| Ramayana in Other Language ||
Ramayana – Tamil Version – by Tamil Maanthan – Read Here
Ramayana – Kannada Version – Sundar khand | Uttara Khand | Kishkindha Khand | Bal khand | Ayodhya Khand 01 & 02 | Yudhdha Khand 01 & 02
Vasista Ramayana – Bengali Version – by P.C. Nahar – Volume 01 | Volume 02
Ramayana Saroddharamu – Telugu Version – by brahmasri Mulukutla Narasimhavadhanulu – Balakanda 01 & 02 | Sundara Kanda | Aranya Kanda | Kishkindha Kanda | Yuddha Kanda 01 & 02 | Uttara Kanda 01 & 02
Ramayana – Malayalam Version – Bala Kanda | Ayodhya Kanda | Aranya Kanda | Kishkindha Kanda | Sundara Kanda | Yuddha Kanda | Uttara Kanda
|| Related Reading ||
Sri Valmiki Ramayana Digdarshan ( Sanskrit Text With Hindi Trans.) By Nathuram Gupta – Read Here
Valmiki’s Ramayana and the natyasastra – English Version – by Bharat Gupt – Read Here
Ramayana Aur Bharata Sanskriti Of Prabodha Chandra Sen, Hindi Trans. By Sumita Sinha, Sanskrit Vidyapeeth Series 62 Shri Lal Bahadur Shastri National Sanskrit University, New Delhi – Read Here
Ramcharitmanas Mein Vaigyanik Tattav – by Dr. Vishnu Datt Sharma – Read Here
Scenes from the Ramayana – English Version – by T.H. Griffith – Read Here
Ramayana Vimarsha – English Version – by T. Amirthalingam – Read Here
Ramayana – Telugu Version – Pocket Books – by Chandamama India Ltd – Read Here
The Ramayana Of Valmeeki – English Version – by Ayyangar & C. R. Sreenivasa – Read Here
Ram Charitmanas Aur Saket Ki Nari Vishyak Avadharana Ka Adhyayna Valmiki Ramayana Ke Pariprekshya Me – Read Here
|| Other Version of Ramayana ||
Sangraha Ramayana – by Bannanje Govindacharya – Volume 01 | Volume 02
Kamba Ramayana – Hindi Version – by Avadhnandan – Read Here – Volume 01 | Volume 02
Sura Ramayana – Hindi Version – by Durga Prasad Khatri – Read Here
Adyathama Ramayana Hindi Anuvadasahitha – by Ranganathan – Read Here
Ranganatha Ramayana – Hindi Version – Shree A.C. Kamakshi Rav – Read Here
Hindi Book Shrimad Valmiki Ramayana(all Kand) – View / Download Here
Jain Ramayana – Hindi Version – by Krishan Lal Verma – Read Here
Champu Ramayana Bhoja Prakasa Sanskrit Hindi Vyakhya Rama Chandra Misra Chowkambha – Read Here
Ramayana / रामायण – 7 Document Collection – by Net Syllabus – View Collection
Ramayana Kakavina ( Indoneshiya Ki Rama Katha) Of Dr. Chandradatta Paliwal Hindi Samiti Granth Mala 270 Uttar Pradesh Hindi Sansthan Lucknow – Read Here
Kashmiri Ramayana Sri Ramavataracarita – English Version – by Divakara Prakasa Bhatia – Read Here
|| Audio Collection of Ramayana ||
Valmiki Ramayana Samhita – Hindi Audio Collection by Vishwas Bhide – Bala Kanda | Ayodhya Kanda | Aranya Kanda | Kishkindha Kanda | Sundara Kanda | Yuddha Kanda | Uttara Kanda | Adhyatma Ramayana
Tulsi Ramayana Samhita – Hindi Audio Collection – Bala Kanda | Ayodhya Kanda | Aranya Kanda | Kishkindha Kanda | Sundara Kanda | Yuddha Kanda | Uttara Kanda | Lanka Kanda
Valmikiya Ramayana – Hindi Audio Collection by Vishwas Bhide – Bala Kanda | Ayodhya Kanda | Aranya Kanda | Kishkindha Kanda | Sundara Kanda | Yuddha Kanda | Uttara Kanda
Ramayane Audio Book in Nepali Language – View Collection
The Ramayana – by Valmiki – Book 01 | Book 02 | Book 03 | Book 04 | Book 05 | Book 06
Ramayana, & Mahabharata Pravachana, Discource – by Dr. K. S. Narayancharya – View Collection
Ramayana – Hindi Version – Sampoorna Srimad Valmiki Ramayana – View Collection
Bhanubhakta Ramayana – Nepali Version (May be) – by Music Nepal – View Collection
Mukesh Sings – by Tulsi Ramayan – Go to Collection
